AI Voice Agent Compliance: TCPA Legal Guide for Voice AI Builders
Key Takeaways
The FCC's February 2024 ruling confirmed AI-generated voice is an "artificial voice" under TCPA—consent is mandatory
Outbound AI voice calls require prior express consent (informational) or prior express written consent (marketing)
The September 2024 FCC NPRM proposes mandatory AI disclosure at the start of every AI-generated call
State laws, including the Colorado AI Act (effective 2026), may classify most voice AI as "high-risk" with significant compliance obligations
TCPA violations carry $500-$1,500 per call penalties with no cap—a 10,000 call campaign = $15M potential exposure
AI voice technology is advancing faster than the regulations designed to govern it. If you're building, deploying, or investing in conversational AI, voice agents, or AI-powered telephony, you're operating in a regulatory environment that's simultaneously uncertain and high-stakes.
Unlike generic AI compliance guides, this resource addresses the specific challenges voice AI builders face: navigating FCC rules that predate modern AI, preparing for state laws like the Colorado AI Act, understanding when inbound vs. outbound matters, and building compliance into your product architecture—not bolting it on after launch.
Why AI Voice Agents Face Elevated Regulatory Risk
AI voice agents sit at the intersection of multiple regulatory frameworks, creating a uniquely complex compliance landscape:
Legacy laws, new technology: The TCPA was written in 1991 to address "robocalls." The FCC is now applying these rules to AI-generated voices that can hold natural conversations—a technology Congress never anticipated.
The "artificial voice" trigger: Any AI-generated voice automatically triggers TCPA's consent requirements, regardless of how human-like it sounds or whether you're using an autodialer.
State law fragmentation: While federal TCPA provides the baseline, states like Colorado, California, and Illinois are layering additional AI-specific requirements on top.
Platform vs. deployer liability: If you're a voice AI platform, your customers' compliance failures may become your liability. If you're deploying someone else's AI, you can't assume the platform has solved compliance for you.
Enterprise deal-breaker: Enterprise buyers increasingly require compliance documentation in RFPs. Compliance gaps don't just create legal risk—they kill deals.
The FCC's Current Framework for AI Voice
February 2024 Declaratory Ruling
In February 2024, the FCC issued a declaratory ruling that removed any ambiguity about AI voice and the TCPA. The ruling confirmed that:
AI-generated voices constitute "artificial or prerecorded voice" under the TCPA
This classification applies regardless of whether the AI generates speech in real-time or uses pre-recorded elements
All existing TCPA consent requirements apply to AI voice calls
State attorneys general can enforce TCPA violations involving AI voice
Critical implication: Even if your dialer isn't technically an "automatic telephone dialing system" (ATDS), you still need consent because the AI-generated voice itself triggers consent requirements. This catches many voice AI builders off guard.
September 2024 NPRM: What's Coming
The FCC's September 2024 Notice of Proposed Rulemaking signals additional requirements on the horizon:
Proposed AI-Generated Call Definition: "A call that uses any technology or tool to generate an artificial or prerecorded voice or text using computational technology or other machine learning, including predictive algorithms and large language models, to process natural language and produce voice or text communication."
Proposed Disclosure Requirements:
Consent disclosure: When obtaining consent, callers must disclose that calls may include AI-generated content
In-call disclosure: AI voice calls must clearly identify themselves as AI-generated at the start of the call
Text message disclosure: AI-generated text messages must include disclosure of AI involvement
Timeline Note: The NPRM comment period closed in late 2024. A final rule could come in 2026, though the current administration's regulatory priorities may delay finalization. Smart builders are implementing these disclosures now—it's where the law is heading, and it builds consumer trust.
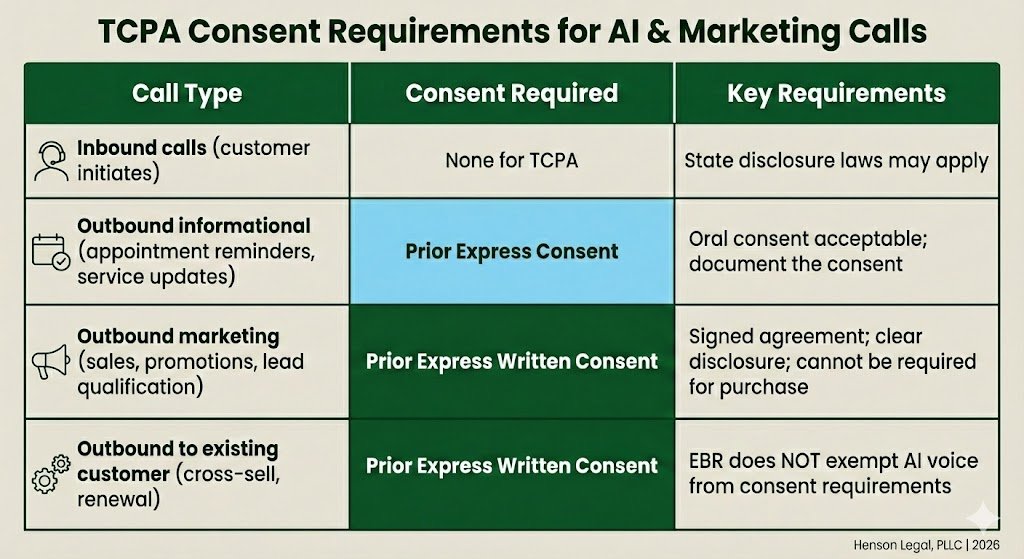
Consent Requirements for AI Voice Calls
The TCPA creates a tiered consent framework. For AI voice calls, consent is always required—the only question is which level.
The AI Voice Consent Matrix
Critical distinction: An Established Business Relationship (EBR) exempts you from Do-Not-Call rules for manual calls—but it does NOT exempt AI voice calls from consent requirements. The AI voice itself triggers the consent obligation, regardless of your existing relationship with the consumer.
Required Disclosures for AI Voice Calls
Under current rules and proposed regulations, AI voice calls must include specific disclosures:
Beginning of Call
Identity of the entity responsible for initiating the call
Identity of the individual caller (if applicable)
[Proposed] Clear disclosure that the call uses AI-generated voice technology
During or After Initial Message
Telephone number of the entity responsible for initiating the call
Within 2 Seconds of Initial Message
Automated, interactive voice- and/or key press-activated opt-out mechanism with brief instructions
State "mini-TCPA" type laws
Many states have "mini-TCPA" type laws which regulate telephone solicitations to the residents of their states. However, some states also have restrictions around the use of "automatic dialing and announcing devices" which are known as ADADs. Depending on the state, these ADADs may encompass the use of AI voice services.
State AI Laws: The Coming Compliance Wave
Colorado AI Act (Effective July 2026)
The Colorado AI Act is the most comprehensive state AI law in the United States. Voice AI builders should assume their products will be classified as "high-risk AI systems" if they make or substantially assist "consequential decisions" affecting consumers.
Why voice AI is likely "high-risk":
Voice agents used for sales qualification make decisions about consumer access to products/services
Customer service agents that escalate or resolve issues affect consumer outcomes
Any voice AI in healthcare, financial services, or insurance is almost certainly high-risk
High-Risk AI Obligations:
Risk management policy and impact assessments
Data governance documentation
Consumer disclosure before consequential decisions
Human oversight mechanisms
Right to human review of adverse decisions
Other State Laws to Watch
Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act: Illinois's law related to the collection, use and handling of biometric identifiers and information by private entities is not the only state law which regulates this sort of data (Texas and Washington do as well), but the Illinois law is the most stringent. The Illinois law includes a private right of action which has led to several class action lawsuits. AI voice providers should be aware of these laws especially when using consumer's voices in a way which may be used to identify the consumer later.
Federal Preemption? The Trump Adminstration has issued an Executive Order designed to pause state level AI laws. However, this Executive Order is likely to be challenged (if not outright ignored).
Wiretapping Laws: Many states require all parties to consent to calls being recorded. AI voice calls are typically recorded and will need to disclose that in the initial call disclosures. Builders should understand which states are “one-party consent” states and which states are “two-party consent” states to adequately get the proper consent.
AI Voice Compliance Implementation Checklist
Consent Infrastructure
Implement consent capture mechanism (web form, in-app, API)
Store consent records with timestamp, IP address, and exact disclosure language
Ensure consent is "clear and conspicuous"—not buried in terms of service
For marketing: Implement signed written consent (e-signature acceptable)
Disclosure Mechanisms
Build AI disclosure into call opening ("This call uses AI-generated voice technology")
Include caller identity and phone number in every call
Implement automated opt-out mechanism within 2 seconds of initial message
Opt-Out & DNC Management
Implement real-time opt-out processing ("immediate" under TCPA)
Maintain internal DNC list with 5-year retention
Scrub against National DNC Registry every 31 days
Documentation & Audit Trail
Log all calls with consent verification status
Record call content (required for some industries)
Maintain consent records for minimum 5 years
Document compliance policies and training
Schedule a 30-minute compliance assessment to review your AI voice product's consent mechanisms, disclosure language, and regulatory exposure.